
Normal: 27 - 31 pg (picamole) weight of RBC.
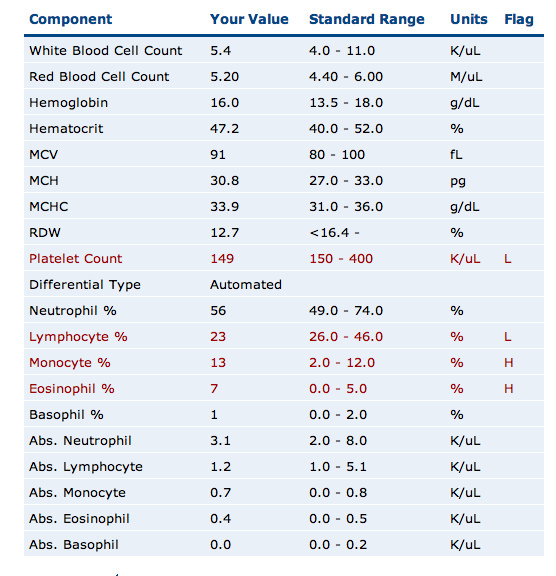 Normal: 80 - 98/um3 (cubic micro meters) Size of RBCĬonditions - pernicious anemia, folic acid anemia, ETOH, liver disease. No IM injections, only use and elctric razorĬheck body orifices for bleeding, guaic stoolįor the Doctor to treat the disease process. Nursing Interventions for Abnormal Platelet ValuesĪpply pressure to venipuncture sites for at least 5 mins. Platelets -part of the hemostatic mechanism is platelet aggregation (clumping), platelets initiate coagulation, life of a platelet 7-9 days, essential for blood clottingĬount of the number of circulation RBC's in 1 mm of peripheral venous blood, part of the complete blood count, produced by erythroid elements in the bone marrow, life of RBC 120 days. & high RBCĭIC=diseminated intravascular coagulation FYI Increased Values: untreated cancer - leukemia, colon cancer, & lymphoma polycythemia vera=high plt. < 20,000 have spontaneous bleeding, hemorrhage, leukemia, DIC, infection, post chemotherapy, ESLD Hematocrit - indirect measure of RBC number & volume, measure of the percentage of total blood volume that is made up of RBCs, Hight of RBC is compaired to the ratio height of the total blood volume, closely reflects the Hgb & RBC values, Hct is 3 times the Hgbĭecreased Values - <100/mm3 have thrombocytopenia, Nursing interventions for Abnormal HGB Values Hemoglobin - transports 02 & C02 in the blood, test determines the 02 carrying capacity of the blood, important to the acid-base buffer system Increased Value - dehydration, COPD, congenital heart disease
Normal: 80 - 98/um3 (cubic micro meters) Size of RBCĬonditions - pernicious anemia, folic acid anemia, ETOH, liver disease. No IM injections, only use and elctric razorĬheck body orifices for bleeding, guaic stoolįor the Doctor to treat the disease process. Nursing Interventions for Abnormal Platelet ValuesĪpply pressure to venipuncture sites for at least 5 mins. Platelets -part of the hemostatic mechanism is platelet aggregation (clumping), platelets initiate coagulation, life of a platelet 7-9 days, essential for blood clottingĬount of the number of circulation RBC's in 1 mm of peripheral venous blood, part of the complete blood count, produced by erythroid elements in the bone marrow, life of RBC 120 days. & high RBCĭIC=diseminated intravascular coagulation FYI Increased Values: untreated cancer - leukemia, colon cancer, & lymphoma polycythemia vera=high plt. < 20,000 have spontaneous bleeding, hemorrhage, leukemia, DIC, infection, post chemotherapy, ESLD Hematocrit - indirect measure of RBC number & volume, measure of the percentage of total blood volume that is made up of RBCs, Hight of RBC is compaired to the ratio height of the total blood volume, closely reflects the Hgb & RBC values, Hct is 3 times the Hgbĭecreased Values - <100/mm3 have thrombocytopenia, Nursing interventions for Abnormal HGB Values Hemoglobin - transports 02 & C02 in the blood, test determines the 02 carrying capacity of the blood, important to the acid-base buffer system Increased Value - dehydration, COPD, congenital heart disease 
Decreased Values: Anemia, dilutional overhydration, cirrhosis, hemorrhage, renal disease








